Discover how to find and analyze various profit margins for stock analysis, including gross, operating, EBIT, pre-tax, net, and free cash flow profit margins.”
Table of Contents
Introduction to Margins
The Importance of Margins in Stock Analysis
Types of Margins
Gross Profit Margin
Operating Profit Margin
EBIT Profit Margin
Pre-tax Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin
Free Cash Flow Profit Margin
Formulas for Margin Analysis
Calculating Margins
Using FinChat.io for Margin Analysis
Conclusion
FAQs
Introduction to Margins
The Importance of Margins in Stock Analysis
When it comes to stock analysis, financial ratios play a crucial role in determining the health and performance of a company. One of the most significant ratios to consider is the profit margin. Profit margins provide an insight into a company's profitability, efficiency, and competitive advantage. A firm with high profit margins demonstrates effective cost control and strong market positioning, which can be a key indicator of potential success and growth.
It is important to understand margins as they flow through financial statements.
But also:
✅ Where they are today
✅ And how they have changed over time as the business becomes more… or less, profitable.
For this analysis, we will use Visa (V) as it is an example of a company with EXCEPTIONAL margins that are best in class of any business, maybe ever.
Types of Margins
There are several types of profit margins that investors should take into account when analyzing a stock. Each margin reflects different aspects of a company's financial health and performance. Let's discuss these margins in detail.
Margins
Gross Profit Margin
- Measures the percentage of revenue exceeding the cost of goods sold (COGS)
- Formula: (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is the ratio of gross profit to revenue. It represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold (COGS). A higher gross profit margin indicates that a company is efficient in managing its production costs and has a strong pricing strategy.
Gross Profit Margin = (Gross Profit / Revenue) x 100
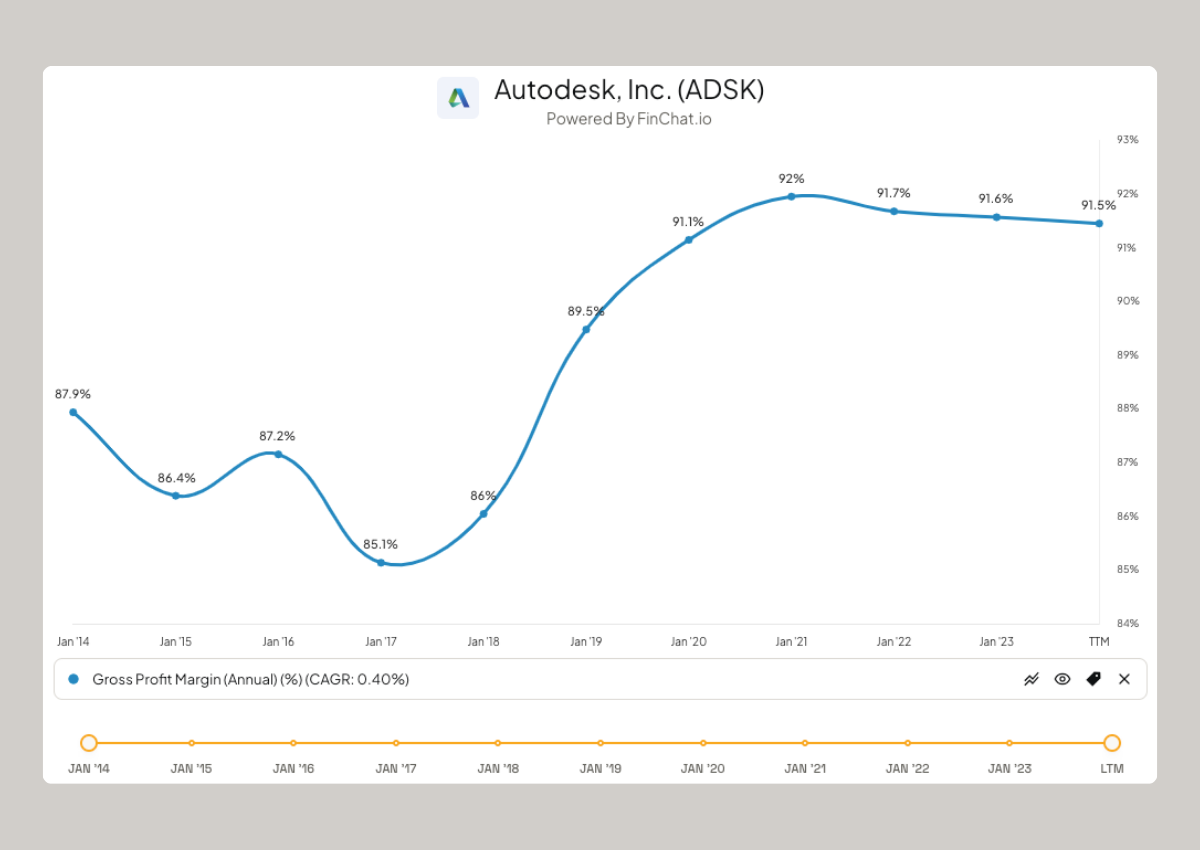
Operating Profit Margin
Operating profit margin is the ratio of operating income to revenue. It measures the percentage of revenue left after deducting the cost of goods sold and operating expenses. A higher operating profit margin demonstrates that a company can effectively manage its operating costs and has a sustainable business model.
Operating Profit Margin = (Operating Income / Revenue) x 100
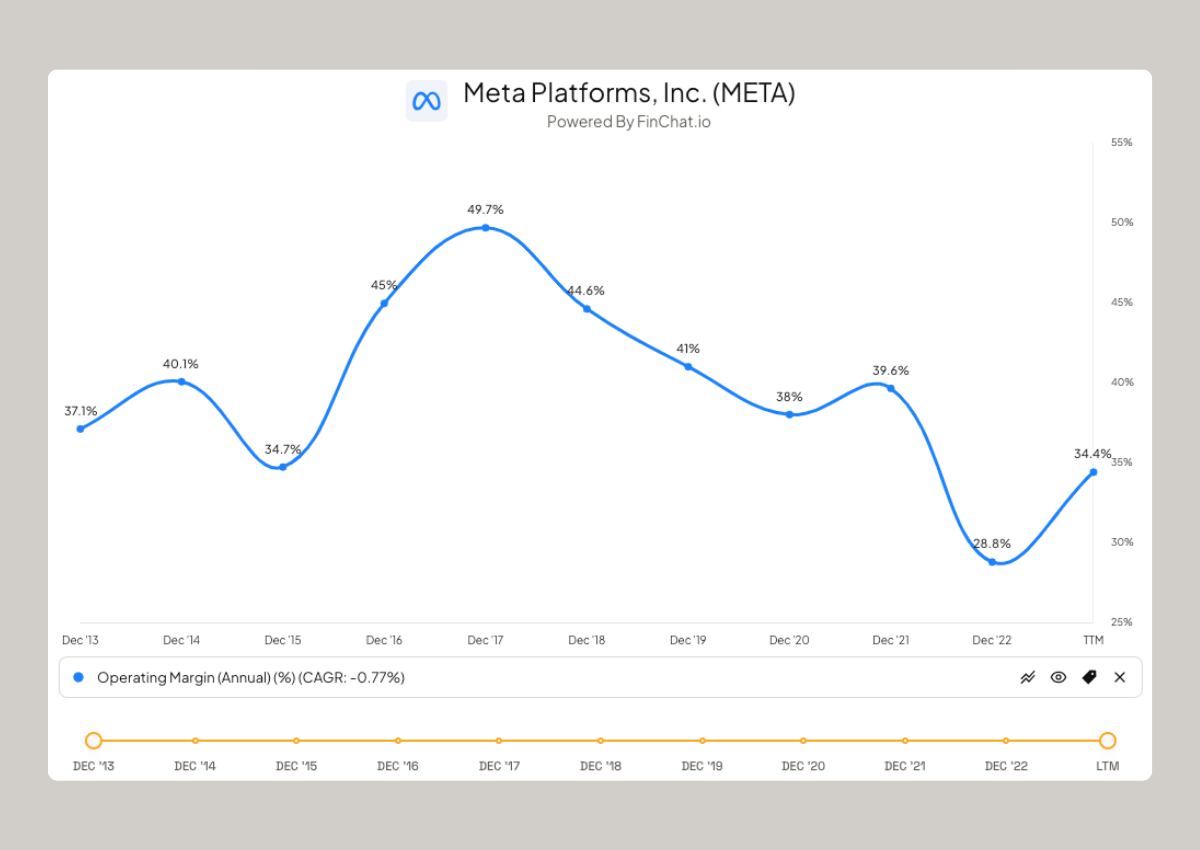
EBIT Profit Margin
EBIT (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes) profit margin is the ratio of EBIT to revenue. It reflects a company's profitability before considering the impact of interest and taxes. A higher EBIT profit margin suggests that a company has a strong operating performance and can generate significant profits.
EBIT Profit Margin = (EBIT / Revenue) x 100
Pre-tax Profit Margin
Pre-tax profit margin is the ratio of pre-tax income to revenue. It measures the percentage of revenue that remains before accounting for income taxes. A higher pre-tax profit margin indicates that a company has a strong financial performance and can generate considerable income before taxes.
Pre-tax Profit Margin = (Pre-tax Income / Revenue) x 100
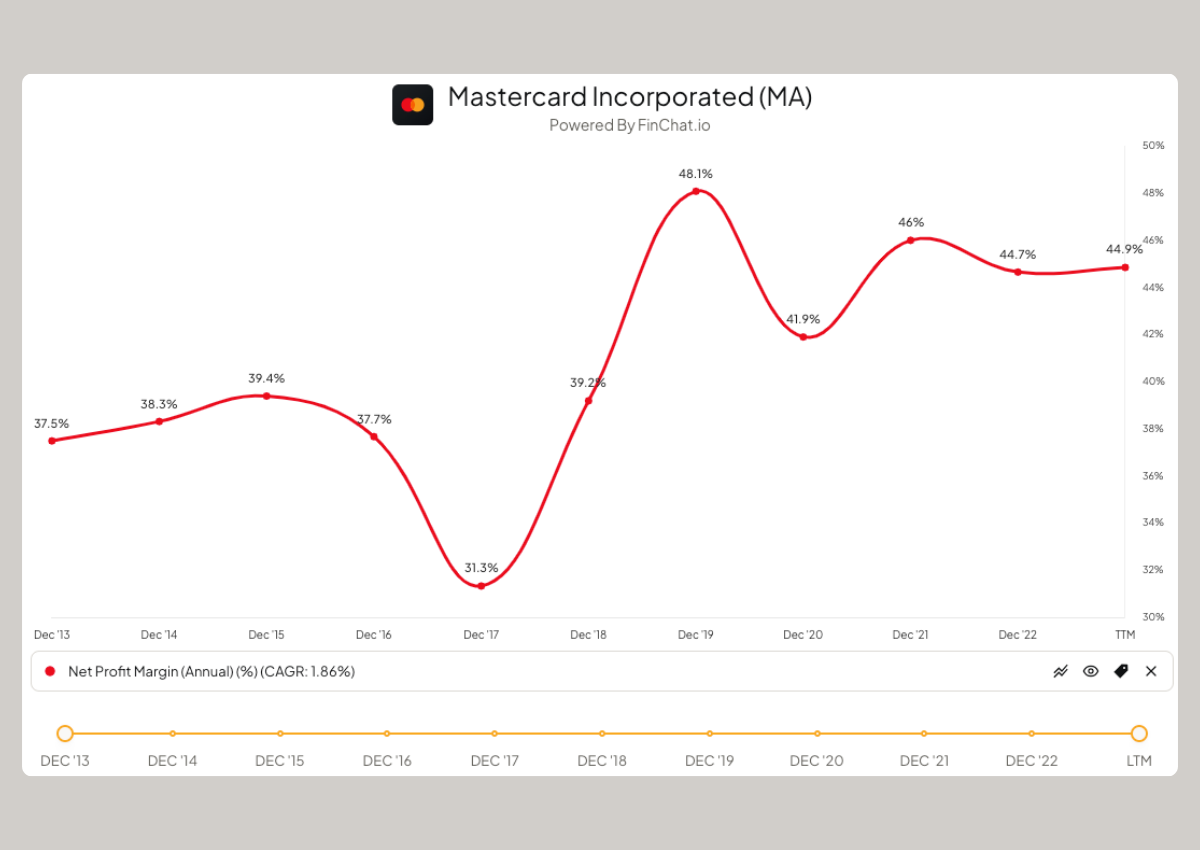
Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin is the ratio of net income to revenue. It represents the percentage of revenue that remains after accounting for all expenses, including taxes. A higher net profit margin demonstrates that a company is efficient in managing its overall costs and can retain a significant portion of its revenue as profit.
Net Profit Margin = (Net Income / Revenue) x 100
Free Cash Flow Profit Margin
Free cash flow profit margin is the
ratio of free cash flow to revenue. It represents the percentage of revenue that remains after accounting for all cash expenses, including capital expenditures and changes in working capital. A higher free cash flow profit margin indicates that a company generates a substantial amount of cash from its operations, which can be used for reinvestment, paying dividends, or reducing debt.
Free Cash Flow Profit Margin = (Free Cash Flow / Revenue) x 100
The types of metrics you will get in summary on FinChat.io company pages
Formulas for Margin Analysis
Calculating Margins
To calculate these margins for stock analysis, use the formulas provided above.
Remember to gather accurate financial data for the company you're analyzing, such as revenue, gross profit, operating income, EBIT, pre-tax income, net income, and free cash flow. These figures can be found in a company's financial statements, such as the income statement and cash flow statement.
Using FinChat.io for Margin Analysis
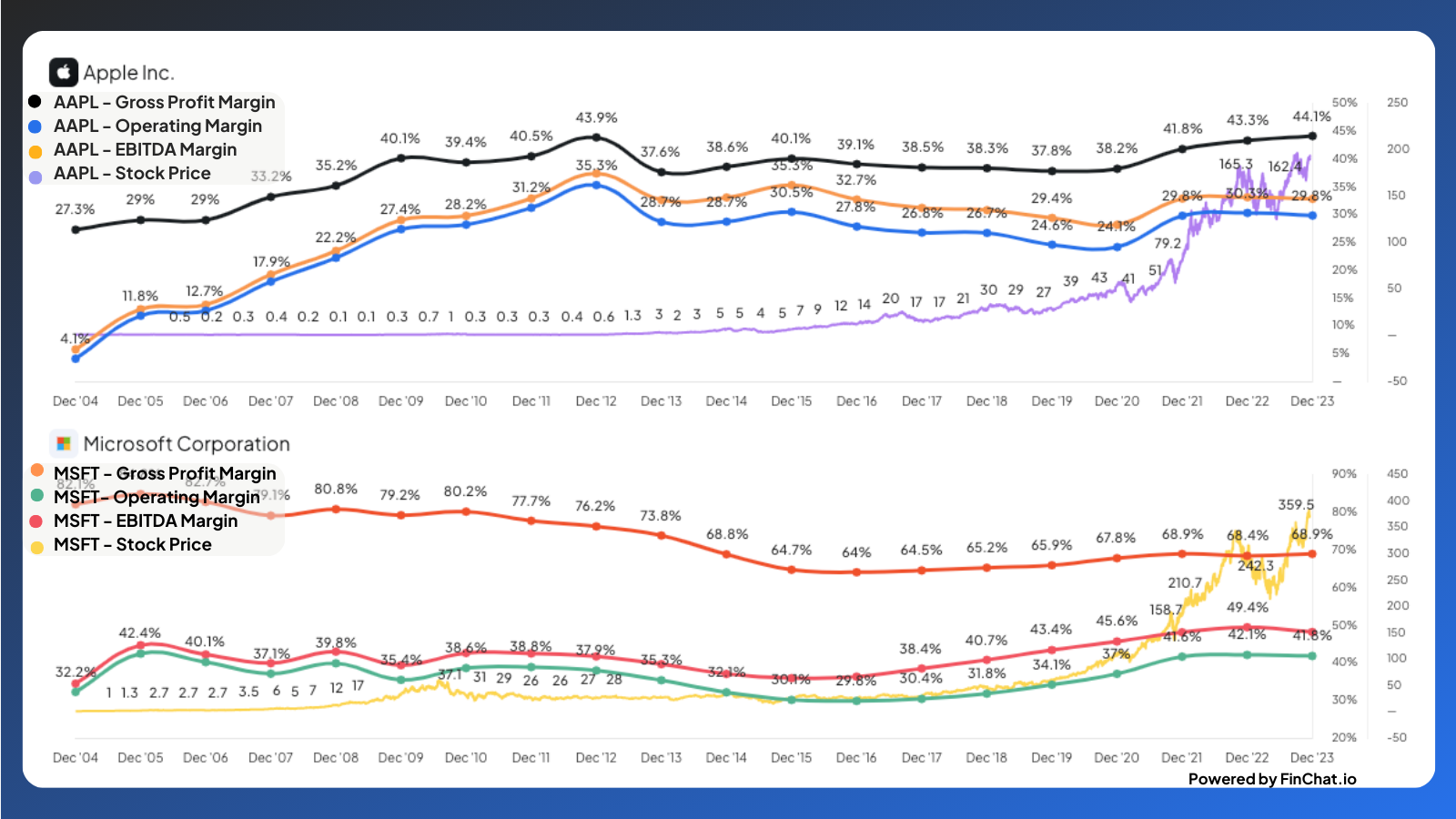
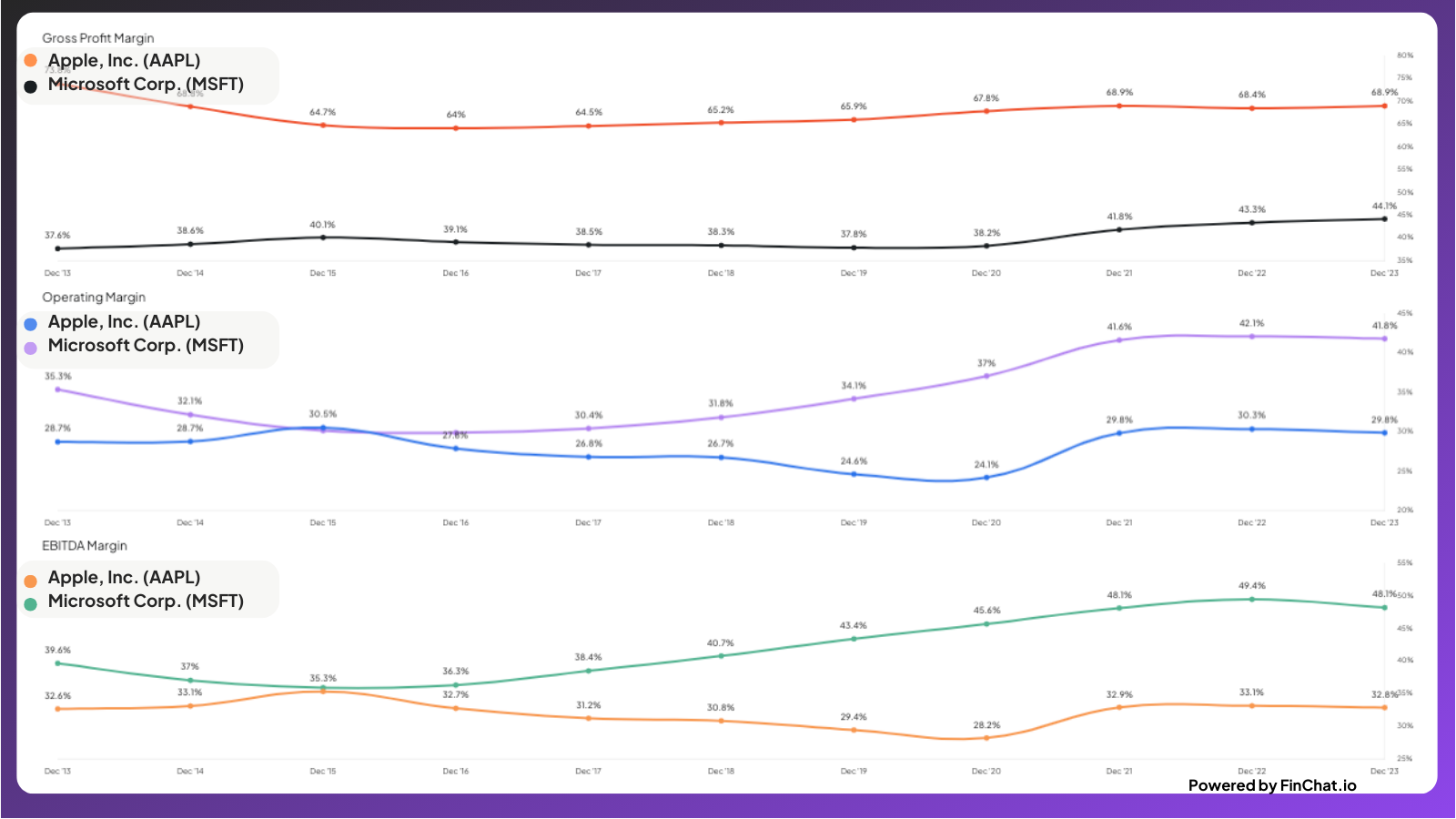
FinChat.io is a valuable resource for investors who want to analyze stock margins. This platform provides all the financial data you need for various stocks, making it easy to calculate margins and evaluate a company's financial performance. Let's look at two examples from FinChat.io - Apple (AAPL) and Microsoft (MSFT).
Apple vs. Microsoft Example
To analyze Apple's financial performance, visit the following link: Apple AAPL
To analyze Microsoft's financial performance, visit the following link: Microsoft MSFT
You can access the two company pages separately which includes revenue, gross profit, operating income, EBIT, pre-tax income, net income, and free cash flow. Utilize the formulas mentioned above to calculate Microsoft's profit margins and evaluate its financial performance.
Or, you can view them side by side with our Fundamental Charting feature.
Conclusion
Analyzing profit margins is a critical aspect of stock analysis that can provide valuable insights into a company's financial health, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
By understanding and calculating various profit margins, investors can make informed decisions about which stocks to invest in. FinChat.io offers an excellent platform to access financial data for numerous stocks, making it easier for investors to perform margin analysis and make informed investment decisions.
FAQs
What is the importance of profit margins in stock analysis?
Profit margins are essential in stock analysis because they provide insights into a company's profitability, efficiency, and competitive advantage. Higher profit margins indicate effective cost control, strong market positioning, and potential for growth.
What are the different types of profit margins?
The different types of profit margins include gross profit margin, operating profit margin, EBIT profit margin, pre-tax profit margin, net profit margin, and free cash flow profit margin.
How do I calculate profit margins?
Use the formulas provided in this article to calculate profit margins, ensuring that you have accurate financial data for the company you're analyzing.
Where can I find financial data for various stocks?
FinChat.io is a valuable resource that offers financial data for numerous stocks, making it easy for investors to calculate margins and evaluate a company's financial performance.
How can I use FinChat.io to analyze profit margins for specific stocks?
Visit the FinChat.io page for the stock you're interested in analyzing, such as Apple or Microsoft.

